torchbox.optim package
Submodules
torchbox.optim.learning_rate module
- class torchbox.optim.learning_rate.LrFinder(device='cpu', plotdir=None, logf=None)
Bases:
object- find(dataloader, model, optimizer, criterion, nin=1, nout=1, nbgc=1, lr_init=1e-08, lr_final=100.0, beta=0.98, gamma=4.0)
Find learning rate
Find learning rate, see How Do You Find A Good Learning Rate .
During traing, two types losses are computed
The average loss is:
\[\rm{avg\_loss}_i=\beta * \rm{avg\_loss}_{i-1}+(1-\beta) * \rm{loss}_i \]The smoothed loss is:
\[\rm{smt\_loss }_{i}=\frac{\rm{avg\_loss}_{i}}{1-\beta^{i+1}} \]If \(i > 1\) and \(\rm{smt\_loss} > \gamma * \rm{best\_loss}\), stop.
If \(\rm{smt\_loss} < \rm{best\_loss}\) or \(i = 1\), let \(\rm{best\_loss} = \rm{smt\_loss}\).
- Parameters:
dataloader (DataLoader) – The dataloader that contains a dataset for training.
model (Module) – Your network module.
optimizer (Optimizer) – The optimizer such as SGD, Adam…
criterion (Loss) – The criterion/loss used for training model.
nin (int, optional) – The number of inputs of the model, the first
ninelements are inputs, the rest are targets(can be None) used for computing loss. (the default is 1)nou (int, optional) – The number of outputs of the model used for computing loss, it works only when the model has multiple outputs, i.e. the outputs is a tuple or list which has several tensor elements (>=1). the first
noutelements are used for computing loss, the rest are ignored. (the default is 1)nbgc (int, optional) – The number of batches for grad cumulation (the default is 1, which means no cumulation)
lr_init (int, optional) – The initial learning rate (the default is 1e-8)
lr_final (int, optional) – The final learning rate (the default is 1e-8)
beta (float, optional) – weight for weighted sum of loss (the default is 0.98)
gamma (float, optional) – The exploding factor \(\gamma\). (the default is 4.)
- Returns:
lrs (list) – Learning rates during training.
smt_losses (list) – Smoothed losses during training.
avg_losses (list) – Average losses during training.
losses (list) – Original losses during training.
Examples
device = 'cuda:1' # device = 'cpu' num_epochs = 30 X = th.randn(100, 2, 3, 4) Y = th.randn(100, 1, 3, 4) trainds = TensorDataset(X, Y) # trainds = TensorDataset(X) model = th.nn.Conv2d(2, 1, 1) model.to(device) trainld = DataLoader(trainds, batch_size=10, shuffle=False) criterion = th.nn.MSELoss(reduction='mean') optimizer = th.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=1e-1) lrfinder = LrFinder(device) # lrfinder = LrFinder(device, plotdir='./') lrfinder.find(trainld, model, optimizer, criterion, nin=1, nbgc=1, lr_init=1e-8, lr_final=10., beta=0.98) lrfinder.plot(lrmod='Linear') lrfinder.plot(lrmod='Log')
- plot(lrmod='log', loss='smoothed')
plot the loss-lr curve
Plot the loss-learning rate curve.
- torchbox.optim.learning_rate.gammalr(x, k=2, t=2, a=1)
torchbox.optim.lr_scheduler module
- class torchbox.optim.lr_scheduler.GaussianLR(optimizer, t_eta_max, sigma1, sigma2, eta_start=1e-06, eta_stop=1e-05, last_epoch=-1)
Bases:
_LRSchedulerSet the learning rate of each parameter group using a double gaussian kernel schedule
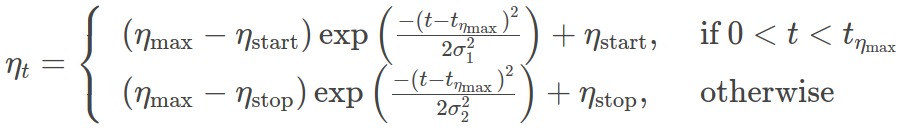
where \(\eta_{max}\) is set to the initial lr and \(T_{cur}\) is the number of epochs since the last restart in SGDR:
When last_epoch=-1, sets initial lr as lr. Notice that because the schedule is defined recursively, the learning rate can be simultaneously modified outside this scheduler by other operators.
The maximum learning rate are the base learning rate setted in Optimizer.
- Parameters:
optimizer (Optimizer) – Wrapped optimizer.
t_eta_max (int) – Iterations when the learning rate reach to the maximum value \(\eta_{\max}\).
sigma1 (int) – Controls the shape of warming up phase.
sigma2 (int) – Controls the shape of annealing phase.
eta_start (float) – Starting learning rate. Default: 0.
eta_stop (float) – Stopping learning rate. Default: 0.
last_epoch (int) – The index of last epoch. Default: -1.
Examples
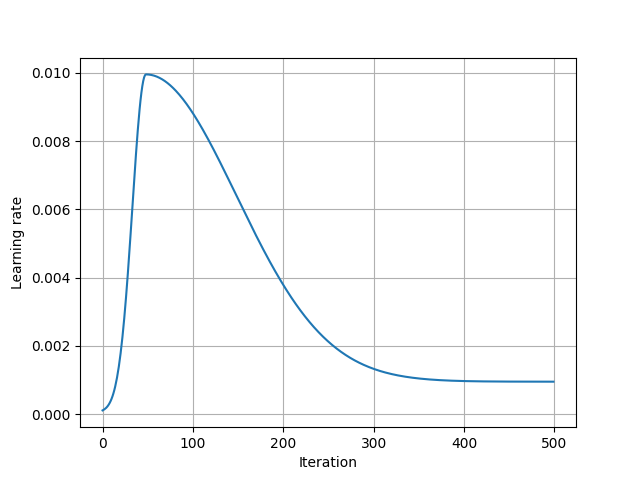
The results shown in the above figure can be obtained by the following codes.
import torch as th import torchbox as tb import matplotlib; matplotlib.use('TkAgg') import matplotlib.pyplot as plt lr = 1e-1 lr = 1e-2 # lr = 1e2 num_epochs = 1000 num_epochs = 500 batch_size = 8 num_batch = 750 params = {th.nn.parameter.Parameter(th.zeros(128), requires_grad=True), th.nn.parameter.Parameter(th.zeros(128), requires_grad=True), } optimizer = th.optim.Adam(params, lr=lr) # optimizer = th.optim.SGD(params, lr=lr, momentum=0.9) scheduler = tb.optim.lr_scheduler.GaussianLR(optimizer, t_eta_max=50, sigma1=15, sigma2=100, eta_start=1e-4, eta_stop=1e-3, last_epoch=-1) print(optimizer) lrs = [] for n in range(num_epochs): for b in range(num_batch): optimizer.step() # lrs.append(optimizer.param_groups[0]['lr']) scheduler.step() lrs.append(optimizer.param_groups[0]['lr']) plt.figure() plt.plot(lrs) plt.xlabel('Iteration') plt.ylabel('Learning rate') plt.grid() plt.show()
- get_lr()
Compute learning rate using chainable form of the scheduler.
- class torchbox.optim.lr_scheduler.MountainLR(optimizer, total_epoch, peak_epoch, period_epoch, last_epoch=-1)
Bases:
_LRSchedulerSet the learning rate of each parameter group using a double gaussian kernel
\[(|x-P| / N) .* (-2 + cos(2 * (x-P) / T)) \]schedule, where \(\eta_{max}\) is set to the initial lr and \(T_{cur}\) is the number of epochs since the last restart in SGDR:
When last_epoch=-1, sets initial lr as lr. Notice that because the schedule is defined recursively, the learning rate can be simultaneously modified outside this scheduler by other operators.
The maximum learning rate are the base learning rate setted in Optimizer.
- Parameters:
optimizer (Optimizer) – Wrapped optimizer.
t_eta_max (int) – Iterations when the learning rate reach to the maximum value \(\eta_{\max}\).
sigma1 (int) – Controls the shape of warming up phase.
sigma2 (int) – Controls the shape of annealing phase.
eta_start (float) – Starting learning rate. Default: 0.
eta_stop (float) – Stopping learning rate. Default: 0.
last_epoch (int) – The index of last epoch. Default: -1.
Examples
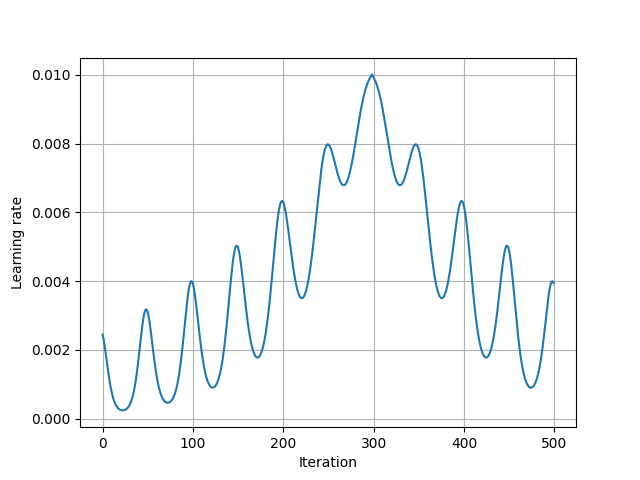
The results shown in the above figure can be obtained by the following codes.
import torch as th import torchbox as tb import matplotlib; matplotlib.use('TkAgg') import matplotlib.pyplot as plt lr = 1e-1 lr = 1e-2 # lr = 1e2 num_epochs = 1000 num_epochs = 500 batch_size = 8 num_batch = 750 params = {th.nn.parameter.Parameter(th.zeros(128), requires_grad=True), th.nn.parameter.Parameter(th.zeros(128), requires_grad=True), } optimizer = th.optim.Adam(params, lr=lr) scheduler = tb.optim.lr_scheduler.MountainLR(optimizer, total_epoch=num_epochs, peak_epoch=300, period_epoch=50, last_epoch=-1) print(optimizer) lrs = [] for n in range(num_epochs): for b in range(num_batch): optimizer.step() # lrs.append(optimizer.param_groups[0]['lr']) scheduler.step() lrs.append(optimizer.param_groups[0]['lr']) plt.figure() plt.plot(lrs) plt.xlabel('Iteration') plt.ylabel('Learning rate') plt.grid() plt.show()
- get_lr()
Compute learning rate using chainable form of the scheduler.
torchbox.optim.mamls_solver module
- class torchbox.optim.mamls_solver.MAML(net, alpha=0.01)
Bases:
object- copy_weights()
- forward(x, adapted_weight=None, **kwards)
- update_base(grads)
- zero_grad()
- class torchbox.optim.mamls_solver.MetaSGD(net)
Bases:
object- copy_weights()
- forward(x, adapted_weight=None, **kwards)
- update_base(grads)
- zero_grad()
- torchbox.optim.mamls_solver.mamls_test_epoch(mmodel, mdl, criterions, criterionws=None, nsteps_base=1, epoch=None, logf='terminal', device='cuda:0', **kwargs)
Test one epoch using MAML, MetaSGD
- Parameters:
mmodel (Module) – the network model
mdl (MetaDataLoader) – the meta dataloader for valid \(\{(x_s, y_s, x_q, y_q)\}\)
nsteps_base (int, optional) – the number of fast adapt steps in inner loop, by default 1
epoch (int or None, optional) – current epoch index, by default
Nonelogf (str or object, optional) – IO for print log, file path or
'terminal'(default)device (str, optional) – device for training, by default
'cuda:0'kwargs – other forward args
- torchbox.optim.mamls_solver.mamls_train_epoch(mmodel, mdl, criterions, criterionws=None, optimizer=None, scheduler=None, nsteps_base=1, epoch=None, logf='terminal', device='cuda:0', **kwargs)
train one epoch using MAML, MetaSGD
- Parameters:
mmodel (Module) – the network model
mdl (MetaDataLoader) – the meta dataloader for training \(\{(x_s, y_s, x_q, y_q)\}\)
optimizer (Optimizer or None) – optimizer for meta learner, default is
None, which meansth.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)scheduler (LrScheduler or None, optional) – scheduler for meta learner, default is
None, which means using fixed learning ratensteps_base (int, optional) – the number of fast adapt steps in inner loop, by default 1
epoch (int or None, optional) – current epoch index, by default
Nonelogf (str or object, optional) – IO for print log, file path or
'terminal'(default)device (str, optional) – device for training, by default
'cuda:0'kwargs – other forward args
- torchbox.optim.mamls_solver.mamls_valid_epoch(mmodel, mdl, criterions, criterionws=None, nsteps_base=1, epoch=None, logf='terminal', device='cuda:0', **kwargs)
valid one epoch using MAML, MetaSGD
- Parameters:
mmodel (Module) – the network model
mdl (MetaDataLoader) – the meta dataloader for valid \(\{(x_s, y_s, x_q, y_q)\}\)
nsteps_base (int, optional) – the number of fast adapt steps in inner loop, by default 1
epoch (int or None, optional) – current epoch index, by default
Nonelogf (str or object, optional) – IO for print log, file path or
'terminal'(default)device (str, optional) – device for training, by default
'cuda:0'kwargs – other forward args
torchbox.optim.save_load module
- torchbox.optim.save_load.device_transfer(obj, name, device)
- torchbox.optim.save_load.get_parameters(model, optimizer=None, scheduler=None, epoch=None)
save model to a file
- Parameters:
- Returns:
keys: ‘epoch’, ‘network’ (model.state_dict), ‘optimizer’ (optimizer.state_dict), ‘scheduler’ (scheduler.state_dict)
- Return type:
- torchbox.optim.save_load.load_model(modelfile, model=None, optimizer=None, scheduler=None, mode='parameter', device='cpu')
load a model from file
- Parameters:
modelfile (str) – the model file path
optimizer (object or None, optional) – the torch.optim.Optimizer, by default
Nonescheduler (object or None, optional) – th.optim.lr_scheduler, by default
Nonemode (str, optional) – the saving mode of model in file,
'model'means saving model structure and parameters,'parameter'means only saving parameters (default)device (str, optional) – load model to the specified device
- torchbox.optim.save_load.save_model(modelfile, model, optimizer=None, scheduler=None, epoch=None, mode='parameter')
save model to a file
- Parameters:
modelfile (str) – model file path
model (object) – the model object or parameter dict
optimizer (object or None, optional) – the torch.optim.Optimizer, by default
Nonescheduler (object or None, optional) – th.optim.lr_scheduler, by default
Noneepoch (int or None, optional) – epoch number, by default
Nonemode (str, optional) – saving mode,
'model'means saving model structure and parameters,'parameter'means only saving parameters (default)
- Returns:
0 is OK
- Return type:
torchbox.optim.solver module
- torchbox.optim.solver.demo_epoch(model, data, bs, logf='stdout', device='cuda:0', odevice='cpu', **kwargs)
Test one epoch
- Parameters:
model (function handle) – an instance of torch.nn.Module
data (tensor or list of tensors) – the data of network inputs
bs (int) – batch size
logf (str or object, optional) – IO for print log, file object or
'stdout'(default)device (str, optional) – device for testing, by default
'cuda:0'odevice (str, optional) – device of output, by default
'cpu'kwargs – other forward args
:param see also
train_epoch(): :paramvalid_epoch(): :paramsave_model(): :paramload_model().:
- torchbox.optim.solver.test_epoch(model, dl, nin, criterions, criterionws=None, epoch=None, logf='stdout', device='cuda:0', **kwargs)
Test one epoch
- Parameters:
model (function handle) – an instance of torch.nn.Module
dl (dataloder) – the testing dataloader
nin (int) – the number of input tensors
criterions (list, tuple or function) – loss function or list/tuple of loss function, e.g. lossfn, [[output_target_pair1_lossf1, output_target_pair1_lossf2], [output_target_pair2_lossf1, output_target_pair2_lossf2], …]
criterionws (list, tuple, float or None) – float loss weight or list/tuple of float loss weight, e.g. w, [[w11, w12], [w21, w22]]
epoch (int or None) – epoch index, default is None
logf (str or object, optional) – IO for print log, file object or
'stdout'(default)device (str, optional) – device for testing, by default
'cuda:0'kwargs – (navg)
'nb'average loss with the number of batchs,'ns'average loss with the number of samples. (…) other forward args
:param see also
train_epoch(): :paramvalid_epoch(): :paramsave_model(): :paramload_model().:
- torchbox.optim.solver.train_epoch(model, dl, nin, criterions, criterionws=None, gclip=None, optimizer=None, scheduler=None, epoch=None, logf='stdout', device='cuda:0', **kwargs)
train one epoch
- Parameters:
model (Module) – an instance of torch.nn.Module
dl (DataLoader) – the dataloader for training
nin (int) – the number of input tensors
criterions (list, tuple or function) – loss function or list/tuple of loss function, e.g. lossfn, [[output_target_pair1_lossf1, output_target_pair1_lossf2], [output_target_pair2_lossf1, output_target_pair2_lossf2], …]
criterionws (list, tuple, float or None) – float loss weight or list/tuple of float loss weight, e.g. w, [[w11, w12], [w21, w22]]
gclip (function) – gradient clip function, default is
None.optimizer (Optimizer or None) – an instance of torch.optim.Optimizer, default is
None, which meansth.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)scheduler (LrScheduler or None) – an instance of torch.optim.LrScheduler, default is
None, which means using fixed learning rateepoch (int) – epoch index
logf (str or object, optional) – IO for print log, file object or
'stdout'(default)device (str, optional) – device for training, by default
'cuda:0'kwargs – (navg)
'nb'average loss with the number of batchs,'ns'average loss with the number of samples. (…) other forward args
:param see also
valid_epoch(): :paramtest_epoch(): :paramsave_model(): :paramload_model().:Examples
import torch as th import torchbox as tb device = 'cuda:0' th.manual_seed(2020) Ns, k, b = 200, 1.5, 3.0 x = th.linspace(0, 10, Ns) t = x * k + b t = tb.awgn(t, snrv=30) deg = (0, 1) model = tb.PolyFit(deg=deg).to(device) dstrain = th.utils.data.TensorDataset(x, t) dltrain = th.utils.data.DataLoader(dstrain, batch_size=50, shuffle=True) dsvalid = th.utils.data.TensorDataset(x, t) dlvalid = th.utils.data.DataLoader(dsvalid, batch_size=20, shuffle=False) criterions = [[tb.SSELoss(reduction='sum'), tb.SSELoss(reduction='sum')]] criterionws = [[1., 0.5]] optimizer = th.optim.Adam(filter(lambda p: p.requires_grad, model.parameters()), lr=1e-2) scheduler = th.optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer, step_size=10, gamma=0.98) for n in range(1000): losstrain = tb.train_epoch(model, dltrain, 1, criterions, criterionws=criterionws, optimizer=optimizer, scheduler=None, epoch=n, logf='stdout', device=device) lossvalid = tb.valid_epoch(model, dlvalid, 1, criterions, criterionws=criterionws, epoch=n, logf='stdout', device=device) scheduler.step() print(model.w[0].item(), model.w[1].item(), scheduler.get_lr()) y = tb.demo_epoch(model, x, 10, logf='stdout', device=device) print(y.shape) plt = tb.plot([[y.cpu(), t]], Xs=[[x, x]], legends=[['Pred', 'GT']]) plt.show() # output --->Train epoch 996, loss: 0.2361, time: 0.01 --->Valid epoch 996, loss: 0.2360, time: 0.01 2.645081043243408 1.5538312196731567 [0.0013532607744362547] --->Train epoch 997, loss: 0.2360, time: 0.01 --->Valid epoch 997, loss: 0.2359, time: 0.01 2.6454339027404785 1.553778886795044 [0.0013532607744362547] --->Train epoch 998, loss: 0.2359, time: 0.01 --->Valid epoch 998, loss: 0.2358, time: 0.01 2.6457810401916504 1.553715705871582 [0.0013532607744362547] --->Train epoch 999, loss: 0.2358, time: 0.01 --->Valid epoch 999, loss: 0.2357, time: 0.01 2.6461341381073 1.5536682605743408 [0.001299671647768579] --->Demo, time: 0.00 torch.Size([200])
- torchbox.optim.solver.valid_epoch(model, dl, nin, criterions, criterionws=None, epoch=None, logf='stdout', device='cuda:0', **kwargs)
valid one epoch
- Parameters:
model (function handle) – an instance of torch.nn.Module
dl (dataloder) – the validation dataloader
nin (int) – the number of input tensors
criterions (list, tuple or function) – loss function or list/tuple of loss function, e.g. lossfn, [[output_target_pair1_lossf1, output_target_pair1_lossf2], [output_target_pair2_lossf1, output_target_pair2_lossf2], …]
criterionws (list, tuple, float or None) – float loss weight or list/tuple of float loss weight, e.g. w, [[w11, w12], [w21, w22]]
epoch (int) – epoch index, default is None
logf (str or object, optional) – IO for print log, file object or
'stdout'(default)device (str, optional) – device for validation, by default
'cuda:0'kwargs – (navg)
'nb'average loss with the number of batchs,'ns'average loss with the number of samples. (…) other forward args
:param see also
train_epoch(): :paramtest_epoch(): :paramsave_model(): :paramload_model().: